Aziridine (Ethyleneimine) is a saturated heterocyclic compound consisting of one amine group in the three-membered ring. The basicity of aziridine is weaker than normal acyclic aliphatic amines. The chemical is a colorless liquid with an intense ammoniacal odor. It has wide applications in the marking of coatings, agricultural products, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, lacquers, and exchanges resins.
Aziridine derivatives are aza-analogs of epoxides. The aziridine functionality is a valuable intermediate in synthetic organic and medicinal chemistry. The three-membered ring structure enables regio- and stereoselective installation of a wide range of functional groups in a 1,2-relationship to nitrogen.1 These compounds are found to have diverse types of biological activity, and involved in synthesis of ring-strain, building blocks in organic synthesis. 2
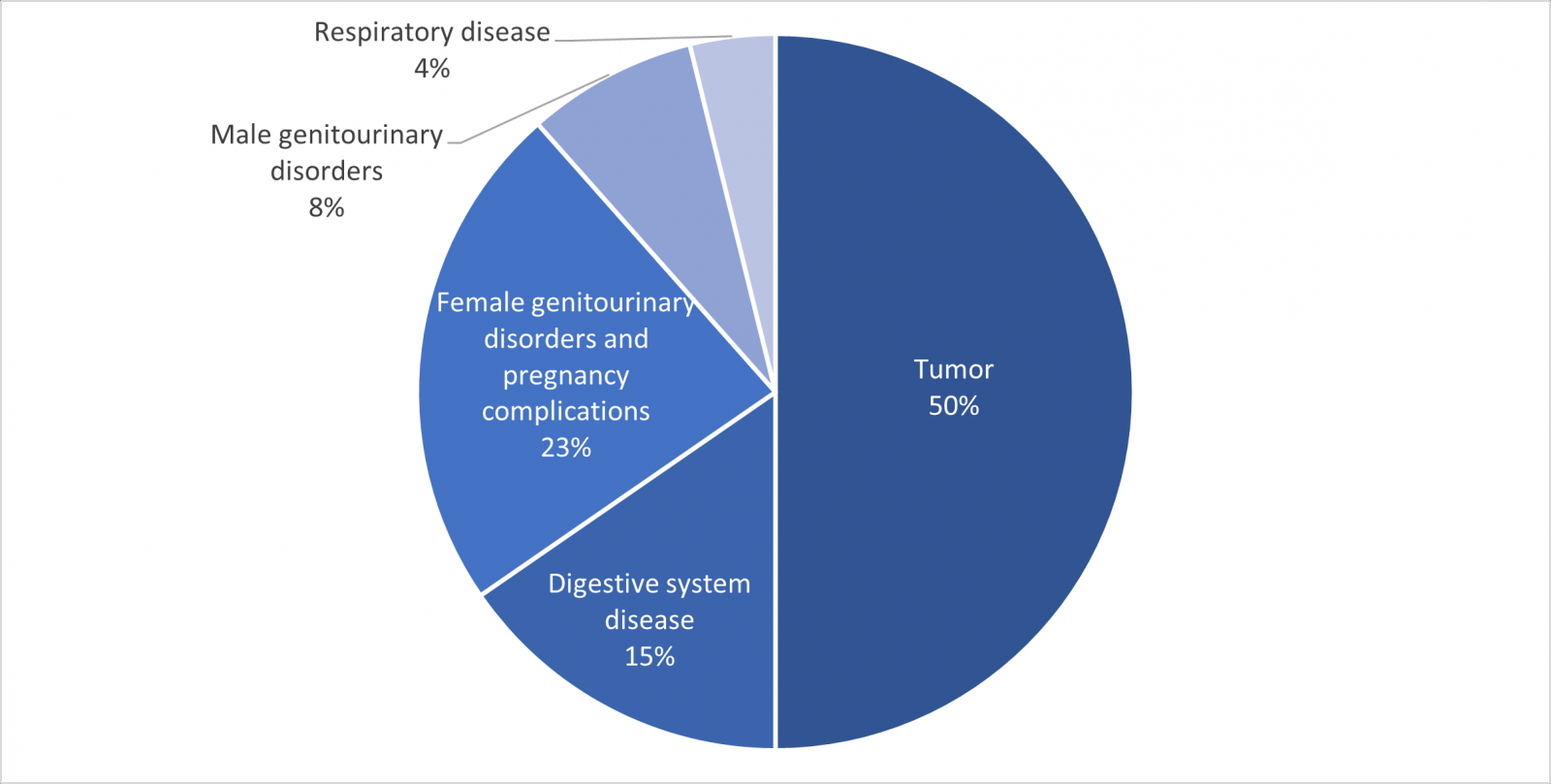
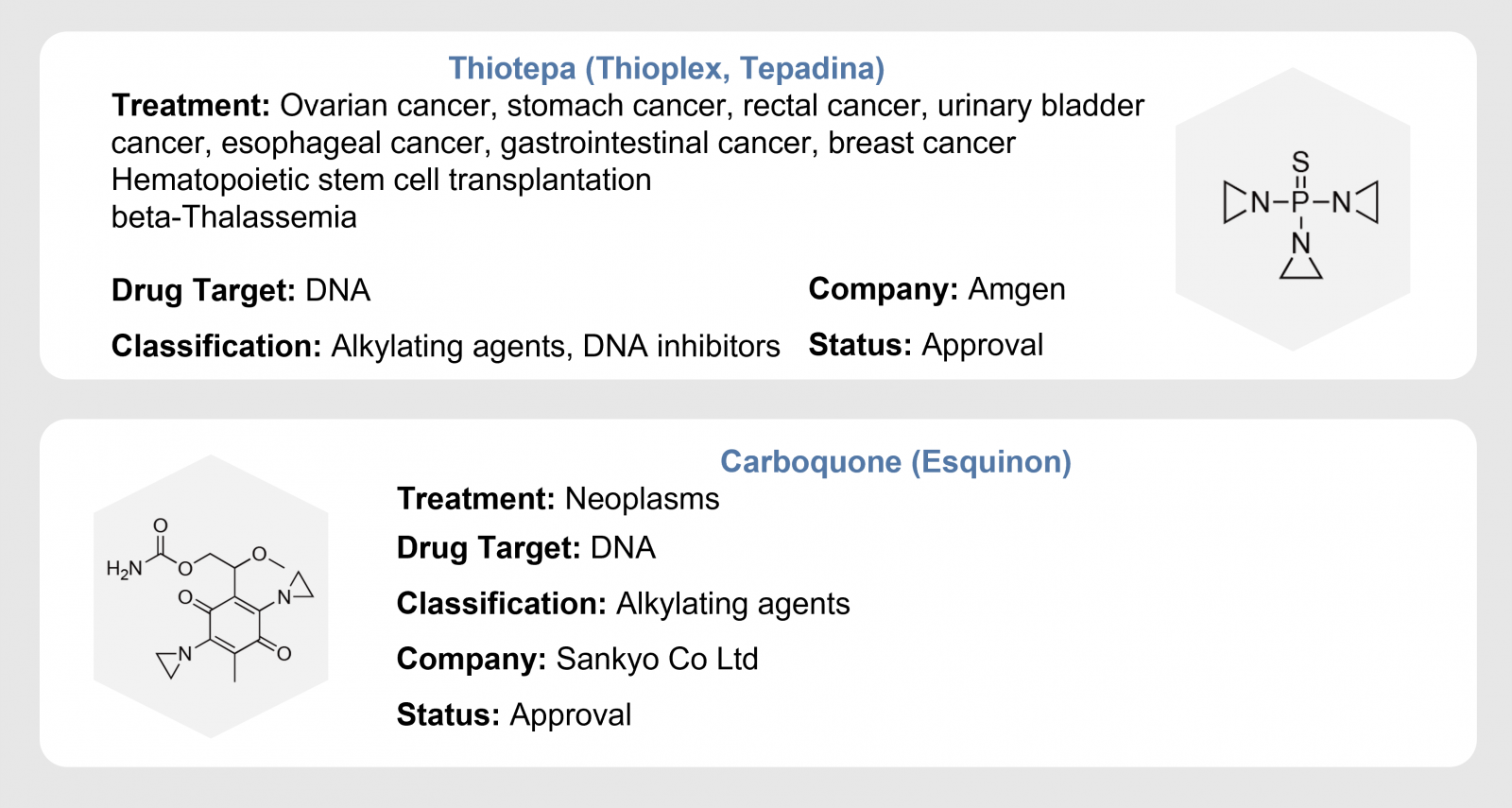
Synthetic compounds containing aziridine ring include cysteine protease inhibitors, antibacterial, antifungal, anticancer, antileishmanial, and antimalarial agents. 3 Some small molecule drugs using aziridine groups are highlighted below. Thiotepa is an alkylating agent used to treat cancer, including breast, ovarian, bladder, and lymphoma cancers. Carboquone is another alkylating agent used in chemotherapy.
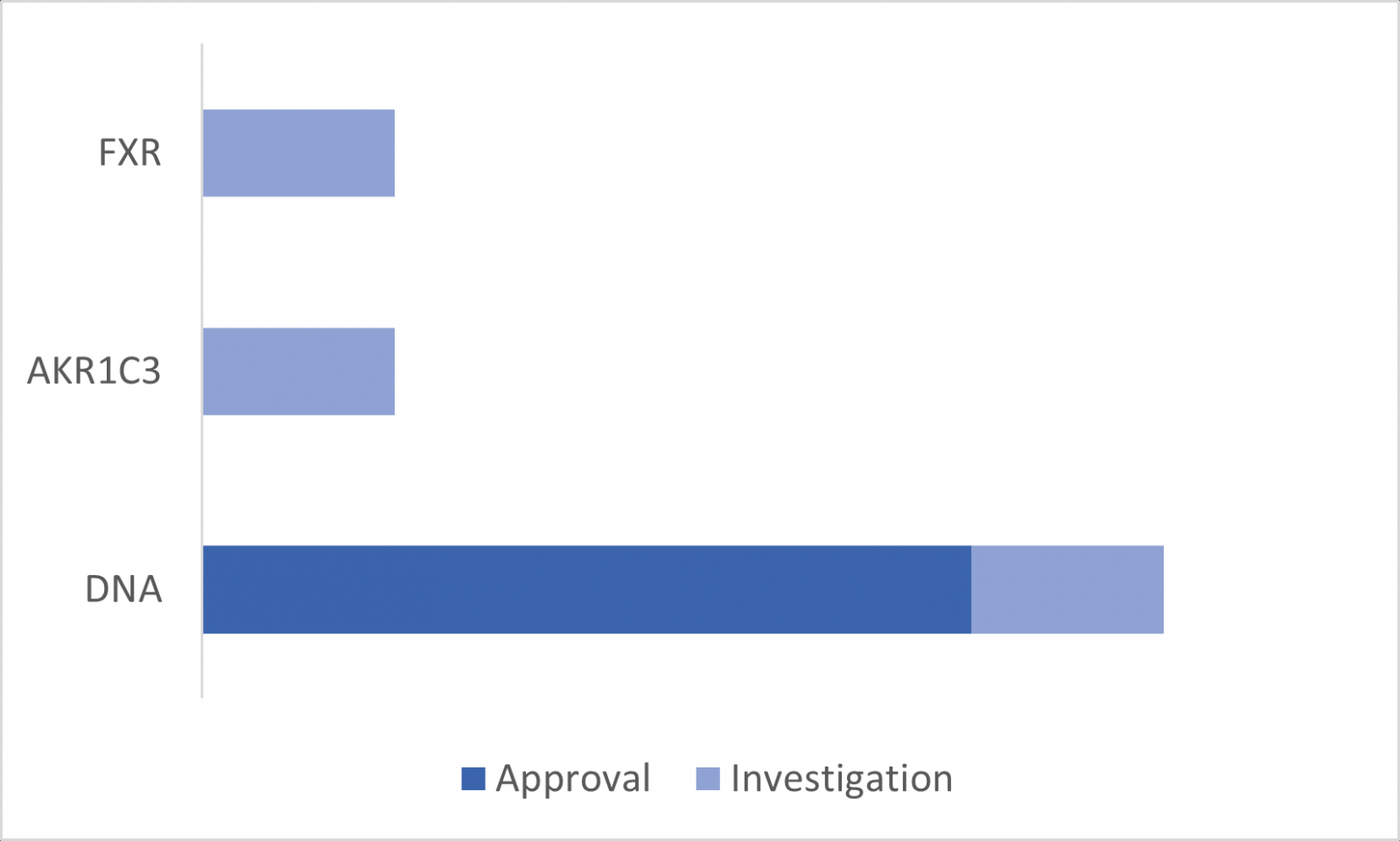
Thiotepa stops the growth of cancer cells by crosslinking guanine nucleobases in DNA double-helix strands. DNA are the most studied targets for aziridines containing drugs. AKR1C3 and FXR are two other drug target options.
Chemenu is a professional supplier of organic building blocks, advanced intermediates, and novel synthetic compounds, including morpholine molecules and custom services.
For aziridine based building blocks, please visit the specific product section https://www.chemenu.com/category/90.html.
(1) Padwa, A. Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry III, 1.01 - Aziridines and Azirines: Monocyclic. Elsevier, 2008, Pages 1-104.
(2) Singh, Girija S. Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry, Chapter Four - Advances in synthesis and chemistry of aziridines. Academic Press, Volume 129, 2019, Pages 245-335.
(3) Singh, Girija S. Synthetic Aziridines in Medicinal Chemistry: A Mini-Review. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2016.16(11):892-904.
Aziridine (Ethyleneimine) is a saturated heterocyclic compound consisting of one amine group in the three-membered ring. The basicity of aziridine is weaker than normal acyclic aliphatic amines. The chemical is a colorless liquid with an intense ammoniacal odor. It has wide applications in the marking of coatings, agricultural products, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, lacquers, and exchanges resins.
CAS 151-56-4
Aziridine derivatives are aza-analogs of epoxides. The aziridine functionality is a valuable intermediate in synthetic organic and medicinal chemistry. The three-membered ring structure enables regio- and stereoselective installation of a wide range of functional groups in a 1,2-relationship to nitrogen.1 These compounds are found to have diverse types of biological activity, and involved in synthesis of ring-strain, building blocks in organic synthesis. 2
Synthetic compounds containing aziridine ring include cysteine protease inhibitors, antibacterial, antifungal, anticancer, antileishmanial, and antimalarial agents. 3 Some small molecule drugs using aziridine groups are highlighted below. Thiotepa is an alkylating agent used to treat cancer, including breast, ovarian, bladder, and lymphoma cancers. Carboquone is another alkylating agent used in chemotherapy.
Thiotepa stops the growth of cancer cells by crosslinking guanine nucleobases in DNA double-helix strands. DNA are the most studied targets for aziridines containing drugs. AKR1C3 and FXR are two other drug target options.
Chemenu is a professional supplier of organic building blocks, advanced intermediates, and novel synthetic compounds, including morpholine molecules and custom services.
For aziridine based building blocks, please visit the specific product section https://www.chemenu.com/category/90.html.
Source:
(1) Padwa, A. Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry III, 1.01 - Aziridines and Azirines: Monocyclic. Elsevier, 2008, Pages 1-104.
(2) Singh, Girija S. Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry, Chapter Four - Advances in synthesis and chemistry of aziridines. Academic Press, Volume 129, 2019, Pages 245-335.
Aziridine (Ethyleneimine) is a saturated heterocyclic compound consisting of one amine group in the three-membered ring. The basicity of aziridine is weaker than normal acyclic aliphatic amines. The chemical is a colorless liquid with an intense ammoniacal odor. It has wide applications in the marking of coatings, agricultural products, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, lacquers, and exchanges resins.
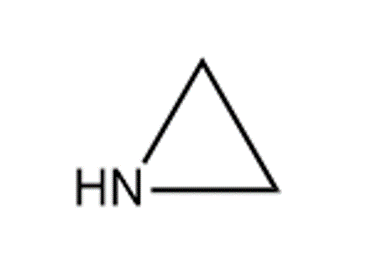
151-56-4
Aziridine derivatives are aza-analogs of epoxides. The aziridine functionality is a valuable intermediate in synthetic organic and medicinal chemistry. The three-membered ring structure enables regio- and stereoselective installation of a wide range of functional groups in a 1,2-relationship to nitrogen.1 These compounds are found to have diverse types of biological activity, and involved in synthesis of ring-strain, building blocks in organic synthesis.2
Synthetic compounds containing aziridine ring include cysteine protease inhibitors, antibacterial, antifungal, anticancer, antileishmanial, and antimalarial agents. 3 A large portion of small molecule drugs using aziridine groups are anti-cancer drugs.DNA are the most studied targets for aziridines containing drugs. AKR1C3 and FXR are two other drug target options.
Some small molecule drugs are highlighted below. Thiotepa is an alkylating agent used to treat cancer, including breast, ovarian, bladder, and lymphoma cancers. Thiotepa stops the growth of cancer cells by crosslinking guanine nucleobases in DNA double-helix strands. Carboquone is another alkylating agent used in chemotherapy.
CHEMENU is a professional supplier of organic building blocks, advanced intermediates, and novel synthetic compounds, including morpholine molecules and custom services.
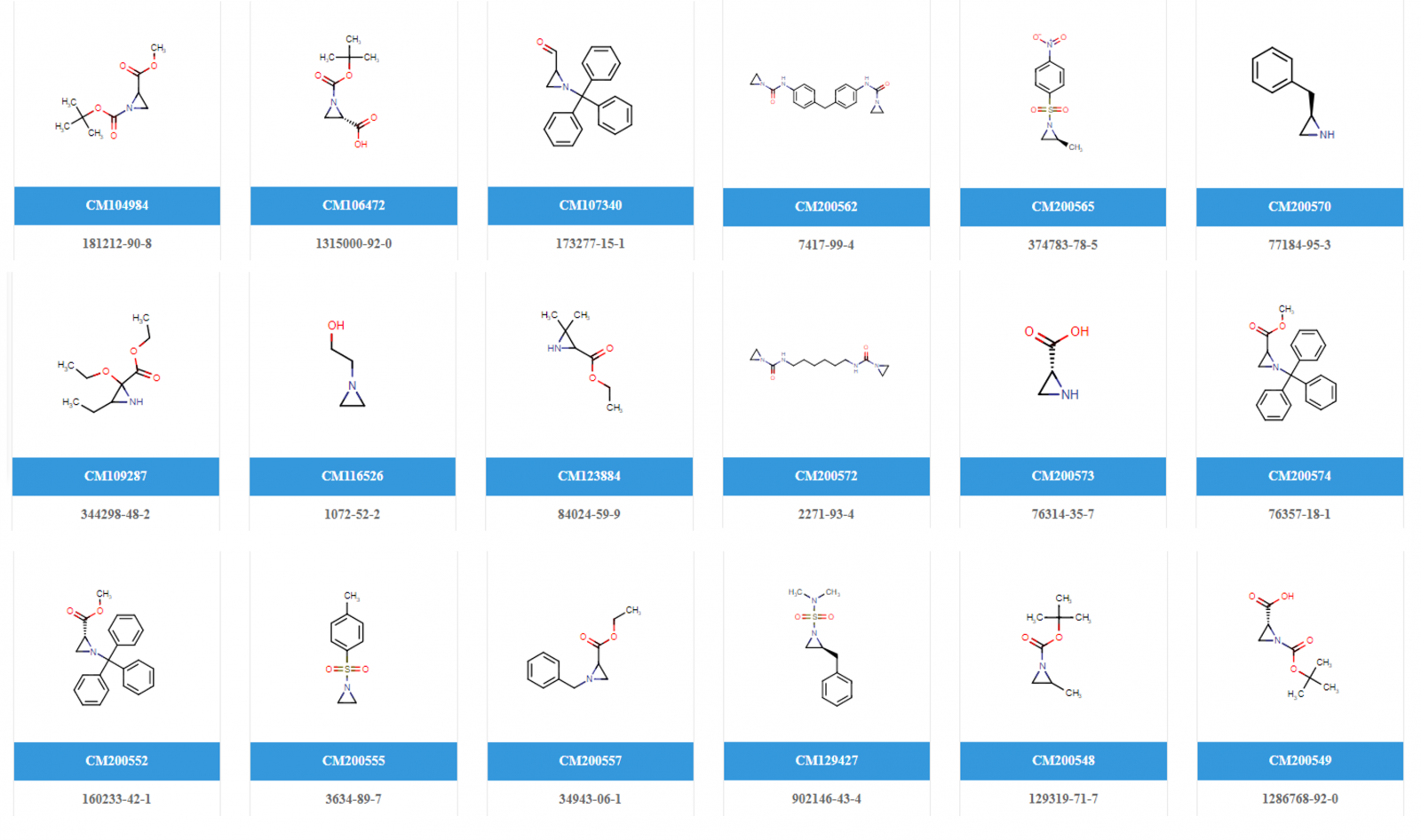
For aziridine based building blocks, please visit the specific product section https://www.chemenu.com/category/90.html.
Source:
(1) Padwa, A. Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry III, 1.01 - Aziridines and Azirines: Monocyclic. Elsevier, 2008, Pages 1-104.
(2) Singh, Girija S. Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry, Chapter Four - Advances in synthesis and chemistry of aziridines. Academic Press, Volume 129, 2019, Pages 245-335.
(3) Singh, Girija S. Synthetic Aziridines in Medicinal Chemistry: A Mini-Review. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2016.16(11):892-904.
CAS 151-56-4
Aziridine derivatives are aza-analogs of epoxides. The aziridine functionality is a valuable intermediate in synthetic organic and medicinal chemistry. The three-membered ring structure enables regio- and stereoselective installation of a wide range of functional groups in a 1,2-relationship to nitrogen.1 These compounds are found to have diverse types of biological activity, and involved in synthesis of ring-strain, building blocks in organic synthesis. 2
Synthetic compounds containing aziridine ring include cysteine protease inhibitors, antibacterial, antifungal, anticancer, antileishmanial, and antimalarial agents. 3 Some small molecule drugs using aziridine groups are highlighted below. Thiotepa is an alkylating agent used to treat cancer, including breast, ovarian, bladder, and lymphoma cancers. Carboquone is another alkylating agent used in chemotherapy.
Thiotepa stops the growth of cancer cells by crosslinking guanine nucleobases in DNA double-helix strands. DNA are the most studied targets for aziridines containing drugs. AKR1C3 and FXR are two other drug target options.
Chemenu is a professional supplier of organic building blocks, advanced intermediates, and novel synthetic compounds, including morpholine molecules and custom services.
For aziridine based building blocks, please visit the specific product section https://www.chemenu.com/category/90.html.
Source:
(1) Padwa, A. Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry III, 1.01 - Aziridines and Azirines: Monocyclic. Elsevier, 2008, Pages 1-104.
(2) Singh, Girija S. Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry, Chapter Four - Advances in synthesis and chemistry of aziridines. Academic Press, Volume 129, 2019, Pages 245-335.
(3) Singh, Girija S. Synthetic Aziridines in Medicinal Chemistry: A Mini-Review. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2016.16(11):892-904.






