Anthracene is a colorless crystalline aromatic hydrocarbon used in the chemical industry and is produced by distilling natural crude oil. This blog will explore its structure, the reactions it undergoes, its uses and hazards.
Aromatic compounds
Anthracene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with three thickly packed benzene rings. Sarah breaks it down very simply: polycyclic means there is more than one ring, aromatic means the molecule has alternating double single bonds around the ring system, and hydrocarbon means it consists of only carbon and hydrogen atoms. We note the three rings connected together, with a network of alternating double and single bonds around the three rings.
9,10-dibromoanthracene
Dimerization of anthracene
If we expose anthracene to UV light, it will actually undergo what is called a dimerization reaction. This is when two anthracene molecules combine with each other to form a larger hydrocarbon structure.
In terms of applications, compounds such as anthracene dimers and other polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons play an important role in organic semiconductors. In addition, they have received a great deal of attention from researchers as organic materials that can be used in solar panels to harness the sun's energy.
Oxidation of anthracene
If anthracene is reacted with an oxidizing agent such as hydrogen peroxide, the product we get is anthraquinone. Anthraquinone is easy to identify; it is simply anthracene with two carbon-oxygen double bonds on the two middle carbons of the molecule.
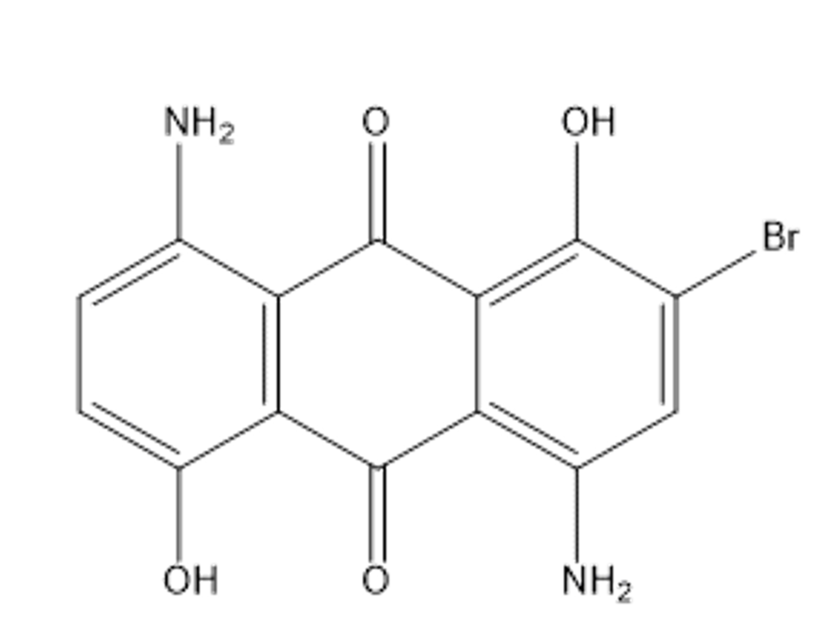
4,8-diamino-2-bromo-1,5-dihydroxy-9,10-dihydroanthracene-9,10-dione
Uses of anthracene
Some of the most common applications of anthracene include use as a preservative for wood and timber and as a pesticide for crops.
The product anthraquinone is actually used as a component of many of the dyes that the fabric and textile industries rely on for their vibrant colors.
Anthracene is used as a scintillator for high-energy photon, electron and alpha particle detectors. Plastics, such as polyethylene-based toluene, can be doped with anthracene to create a water-equivalent plastic scintillator for radiation therapy dosimetry.
Anthracene is widely used as a UV tracer in conformal coatings for printed circuit boards. Anthracene tracers allow UV detection of conformal coatings. Anthracene is also used for anthraquinone applications.
Anthracene derivatives are used in many applications. 1-hydroxyanthracene and 2-hydroxyanthracene are hydroxylated derivatives of phenol and naphthol, and hydroxyanthracene (also known as anthracenol and anthracenol) has pharmacological activity. 9,10-dihydroxyanthracene is an example of anthracene with several hydroxyl groups.
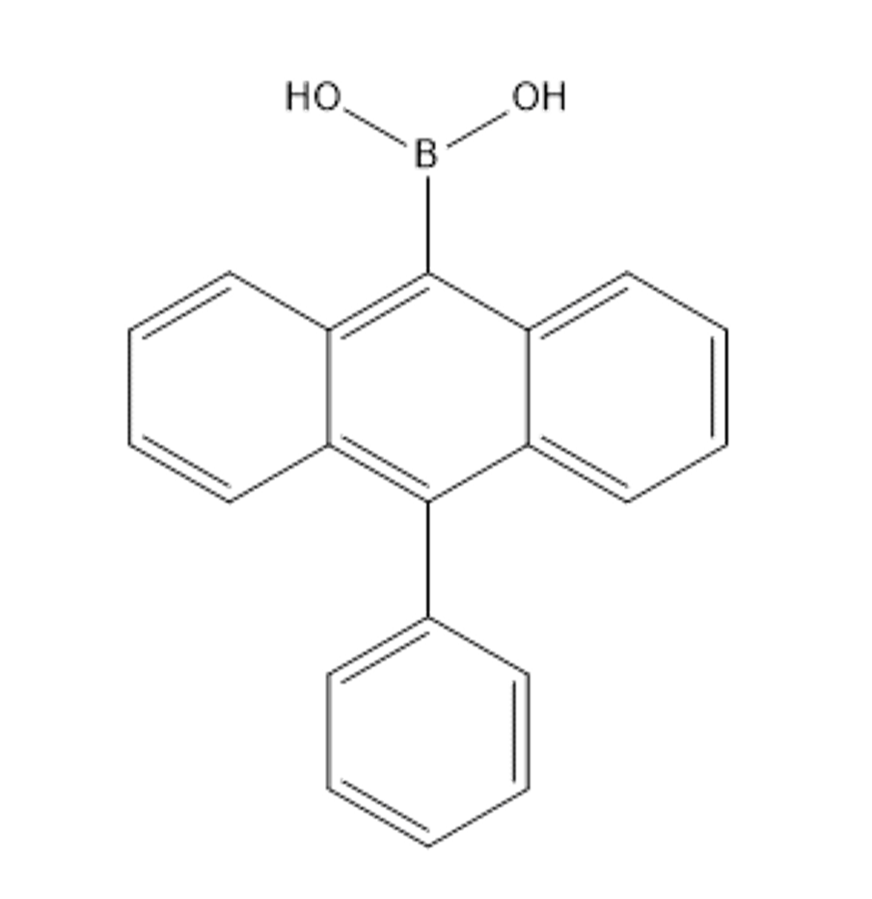
(10-phenylanthracen-9-yl)boronic acid
Attention to hazards
Anthracene is a non-carcinogenic substance. PAHs are considered to be potential starting materials for the abiotic synthesis of materials needed for the earliest forms of life. When inhaled, anthracene can irritate the throat, nose and lungs, causing wheezing and coughing. Contact with the skin may cause irritation, burns, and itching caused by sunlight. Frequent exposure may lead to skin thickening and pigmentation changes. Studies have shown that anthracene may become allergic, and once the allergy is fully developed in an individual, even very low future exposures can cause a rash.
Please note that local exhaust ventilation is used in areas where chemicals are released. If local exhaust ventilation is not appropriate for the job, make sure you use a respirator that is easy to wear.